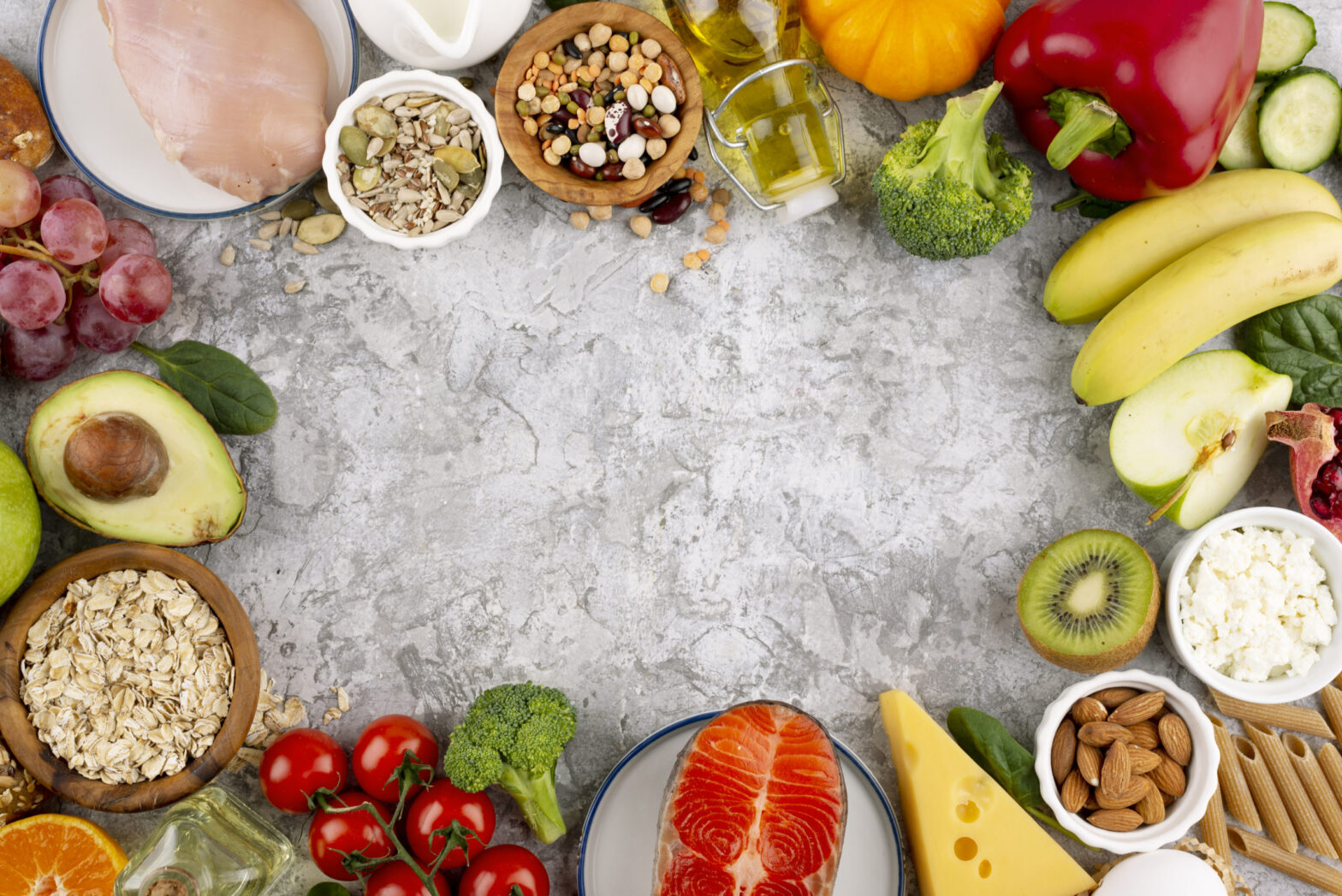
Proper nutrition is vital for a healthy life and even for nations that want to advance and prosper. However, ironically, undernutrition is a big issue affecting much of India’s population. The problem is so huge that, according to Poshan, high levels of adult undernutrition affect one-third of the country’s adults. This issue is often linked to poverty and a lack of access to quality food. However, many times it is also due to a lack of knowledge.
In this content piece, we are going to talk about one such topic: the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients. This information is also important for individuals taking nutrition classes. Orane runs more than 100 institutes in India, and there have been observations that this question sometimes confuses even the best minds. So, let’s address it!
What Are Macronutrients and Their Functions?
Macronutrients are the nutrients our bodies require in large quantities to fulfill our energy needs. They are the building blocks that fuel our bodies and support various bodily functions. The three primary macronutrients are:
- Carbohydrates: These act as the body’s main source of energy. And you can find them in foods like grains, fruits, and vegetables (bread, beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, spaghetti, etc.). Carbohydrates provide quick energy and exist in simple and complex forms. Simple carbohydrates like sugar are easily digested and absorbed, boosting energy. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, release energy slowly, ensuring a sustained energy supply.
- Proteins: Proteins are crucial for developing, repairing, and maintaining body tissues. They consist of amino acids and are present in foods like meat, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts. Proteins play a vital role in building and repairing muscle, supporting the immune system, and producing enzymes and hormones.
- Fats: Fats are essential for our bodies to function properly, providing insulation and protection for organs and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. While fats have a bad reputation, it’s important to differentiate between healthy fats, such as those found in avocados and nuts, and unhealthy fats, like saturated and trans fats, found in processed foods and fast food.
Understanding Micronutrients and Their Advantages
As the name suggests, micronutrients are nutrients required in smaller quantities but equally important for our overall health. They include vitamins, calcium, minerals, etc., which play vital roles in various physiological processes.
1. Vitamins
These are organic compounds our bodies need in small amounts for proper functioning. There are two types of vitamins: water-soluble vitamins (such as vitamin C and B-complex vitamins) and fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K). Each vitamin has specific functions, ranging from supporting our immune system to promoting healthy vision. One can find them in food sources such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products (meat, poultry, fish, beans. carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, nuts, vegetable oils, etc.). For more information on vitamins, check out this article published in medical news today.
2. Minerals
These are the unsung heroes of our nutrition story inorganic substances that our bodies require for an array of physiological processes. Among them are vital minerals such as calcium, iron, zinc, and potassium, which play pivotal roles in maintaining our overall health. These minerals are found in diverse foods, from meat and cereals to fish, milk, dairy products, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Their contributions to our well-being encompass bone health, muscle function, nerve transmission, and the delicate balance of electrolytes in our systems.
Here are some of the most important minerals and their functions:
- Calcium: This essential mineral helps build and maintain strong bones and teeth and plays a vital role in muscle function and blood clotting. Calcium is a multitasker found in dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods.
- Iron: As the body’s oxygen courier, iron is indispensable. It not only helps carry oxygen throughout the body but also aids in the production of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying molecule in red blood cells. You can find this vital mineral in red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and dark leafy greens, making it a cornerstone of your diet.
- Magnesium: Beyond its role in maintaining strong bones and muscles, magnesium is a true regulator. It helps control blood sugar levels, supports nerve function, and checks blood pressure. This versatile mineral can be sourced from whole grains, nuts, seeds, and green vegetables.
- Potassium: Your heart’s best friend, potassium, helps regulate blood pressure and plays a crucial role in maintaining proper heart function. It’s abundantly present in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products (dried fruits like raisins, apricots, beans, lentils, and potatoes; winter squash; broccoli, etc.).
- Zinc: Consider zinc your body’s defender. It assists in the immune system’s battle against infections and contributes to hormone production. This mighty mineral can be found in meat, poultry, fish, and nuts, reinforcing its importance in your overall health strategy.
Now that we’ve delved into the world of minerals and their importance, it’s evident that these micronutrients are the unsung heroes quietly orchestrating our well-being. Now let’s understand how to get the right balance of them along with macronutrients.
How to Get the Right Macronutrient-Micronutrient Balance in Your Diet
The best way to get the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients in your diet is to eat a variety of whole, unprocessed foods. These foods are naturally rich in nutrients and provide our bodies with everything they need to function properly.
Here are some unprocessed food choices you should integrate into your diet:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean protein
- Low-fat dairy products
- Nuts and seeds
Limiting our intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats is also important. These foods are often high in calories and low in nutrients, and they can contribute to weight gain, chronic diseases, and other health problems.
If you’re not sure how to create a healthy diet, talk to a registered dietitian or qualified healthcare professional. They can help you develop a personalized plan that meets your individual needs and goals. Moreover, if you are interested in becoming a certified nutritionist, consider Orane’s comprehensive nutrition course range.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients is essential for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet. Macronutrients provide us with the energy we need, while micronutrients support our bodies in various physiological processes. By incorporating a variety of foods rich in both macronutrients and micronutrients, we can ensure that our bodies receive the necessary nourishment for optimal health. Remember, a well-informed approach to nutrition is the key to a vibrant and energetic life!